Physical Properties |
|
| Chemical formula | CaMg(CO3)2 |
| Class | Carbonate |
| Crystal system | Hexagonal (rhombohedral) |
| Habit | Typically rhombohedral Prismatic Steep rhombohedra Massive |
| Color | Pink White Brown Black Green Gray Colorless |
| Hardness | 3.5 to 4 |
| Specific gravity | 2.85 |
| Cleavage | Perfect rhombohedral {101} |
| Fracture | Subconchoidal |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent |
| Streak | White |
Optical Properties |
|
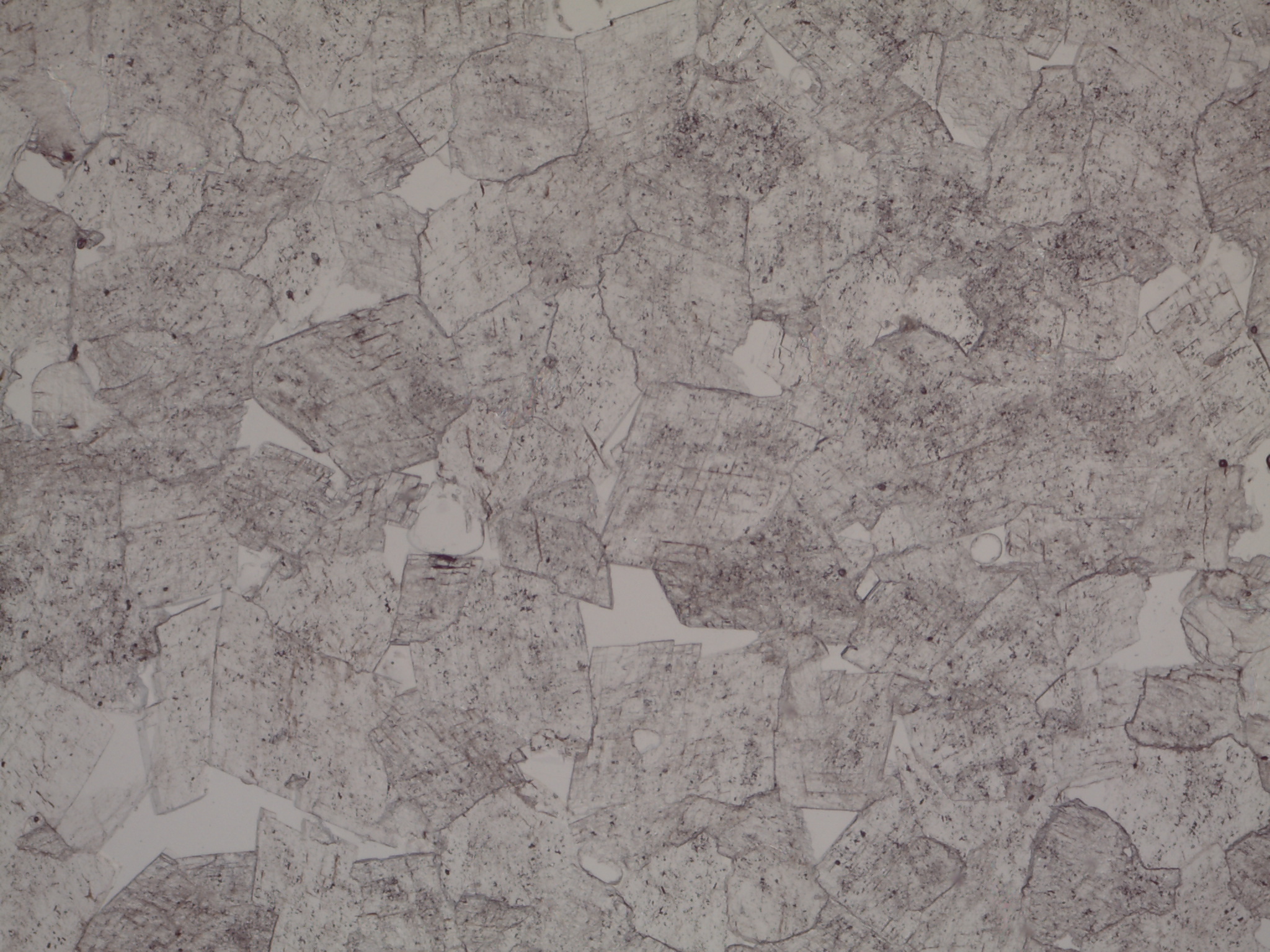
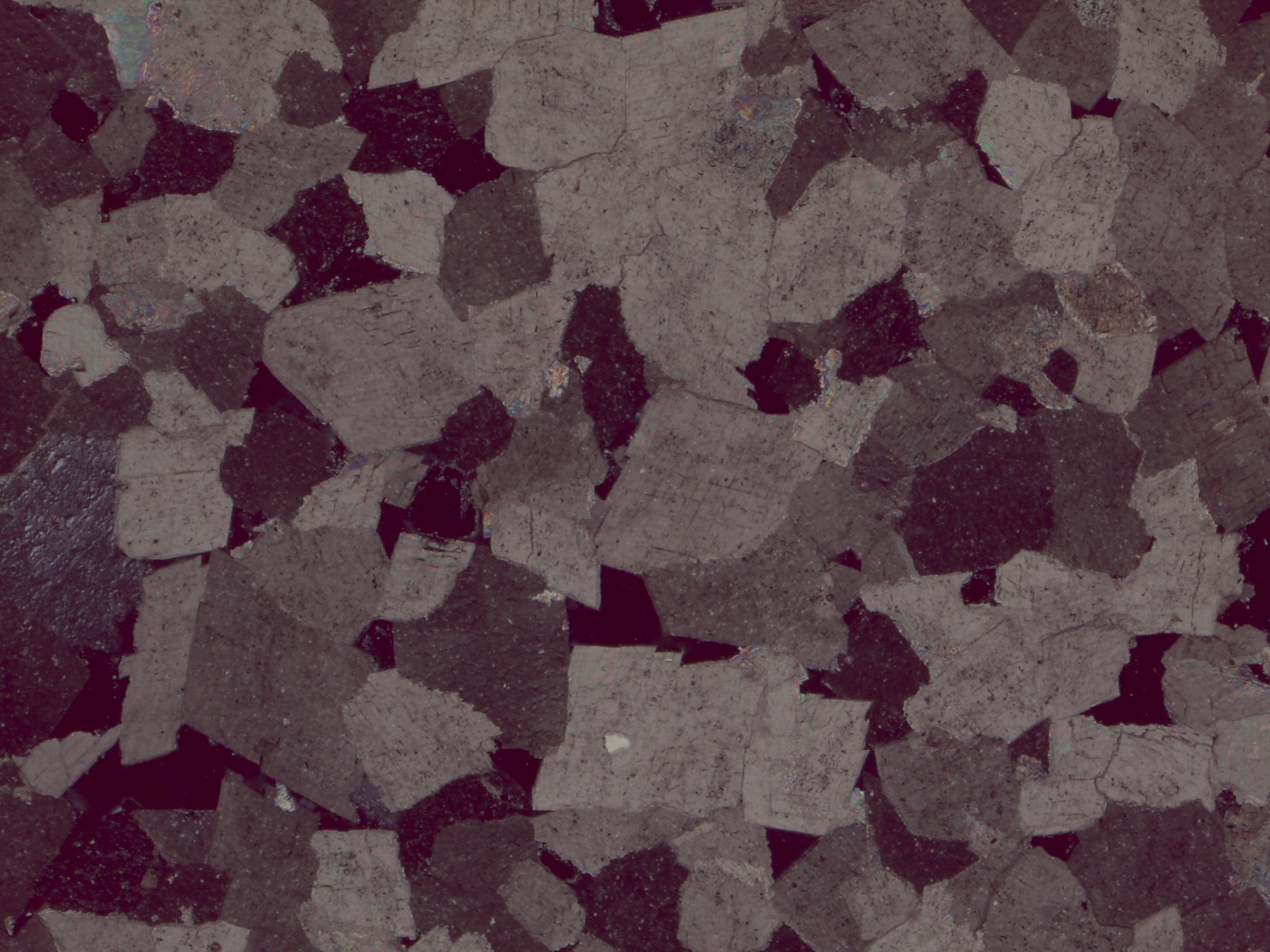
| PPL | Colorless, but may exhibit pale pastels Visible polysynthetic “calcite” twinning in coarse grains |
| XPL | Extremely high birefringence; colors may look pastel, washed out, or almost neon Polysynthetic “calcite” twinning” in coarse grains; fine grains appear as a sort of swirl of color |
| δ | 0.179 |
| Twinning | Lamellar |
| Special properties | Reacts with HCl (fizzes), but only if powdered |
| after Perkins, 384-385 |
Dolomite in Hand Sample
Dolomite
Two small hand samples of dolomite
Differentially weathered calcite and dolomite
Scanning electron micrograph of dolomite
If you’ve taken an intro Geology class (and I bet you have), you’ve probably heard that chalk is made up of the calcite tests of algae called coccolithophores. Well, sometimes it’s true. Sometimes it’s made of a blend of dolomite and gypsum, as seen in this scanning electron micrograph. Sometimes it’s just gypsum, as seen in this scanning electron micrograph.
Dolomite in Thin Section
Thin Section GigaPans
Dolomite in plane polars
Dolomite in crossed polars