Physical Properties |
|
| Chemical formula | CaSO4∙2H2O |
| Class | Sulfate |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Habit | Tabular Elongate masses Rosettes Acicular splays Massive Granular |
| Color | Colorless White Variable |
| Hardness | 2 |
| Specific gravity | 2.32 |
| Cleavage | Perfect basal (010), good (100) and {011} |
| Fracture | Conchoidal |
| Luster | Vitreous Pearly |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent |
| Streak | White |
Optical Properties |
|
| PPL | Colorless Non-pleochroic |
| XPL | Up to 1st order yellows |
| δ | 0.009 |
| after Perkins, 394-395 |
Gypsum in Hand Sample
Gypsum, var. selenite
Another selenite
Scanning electron micrograph of selenite
Gypsum, var. satinspar
Scanning electron micrograph of satinspar
Gypsum, var. alabaster
Gypsum casts in Tonoloway Formation limestone
Scanning electron micrograph of gypsum from Zone 4 of the Calvert Formation
If you’ve taken an intro Geology class (and I bet you have), you’ve probably heard that chalk is made up of the calcite tests of algae called coccolithophores. Well, sometimes it’s true. Sometimes it’s made of a blend of dolomite and gypsum, as seen in this scanning electron micrograph. Sometimes it’s just straight gypsum, as seen in this scanning electron micrograph.
Gypsum in 3D
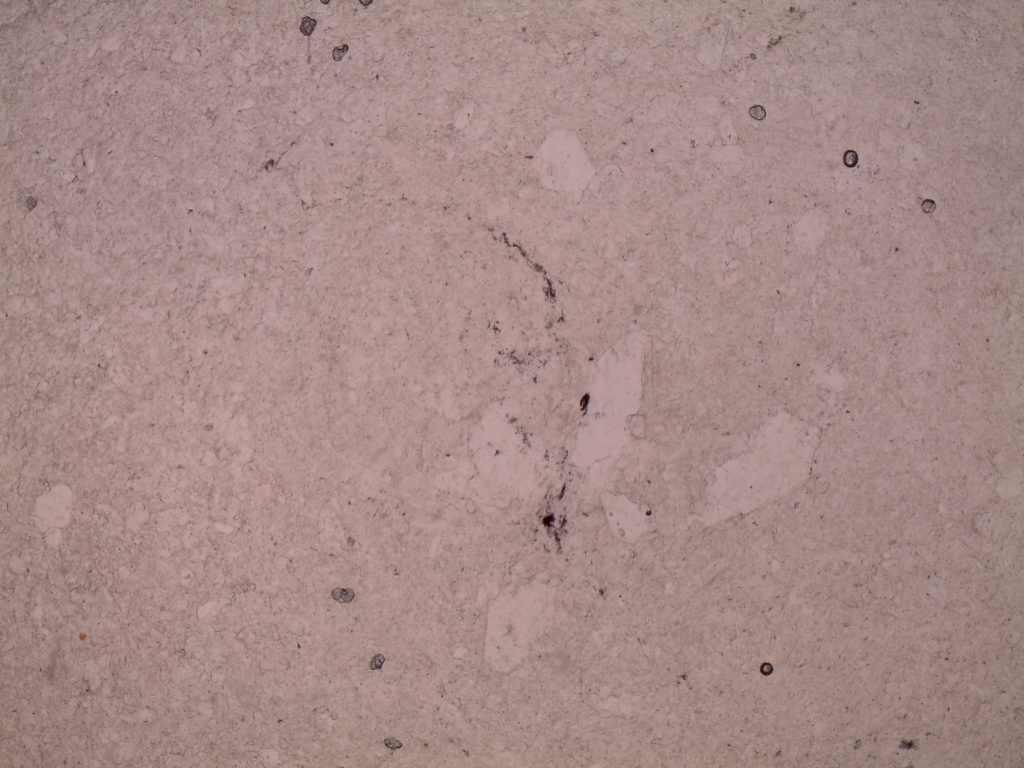
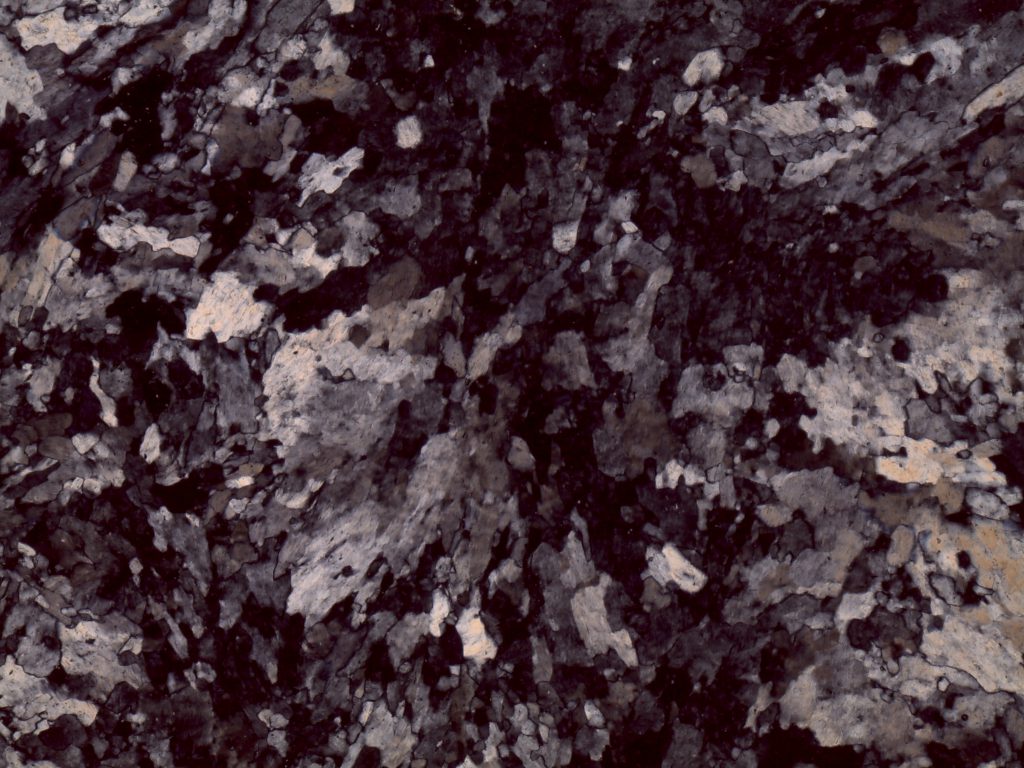
Gypsum, var. alabaster, plane polars
Gypsum, var. alabaster, crossed polars
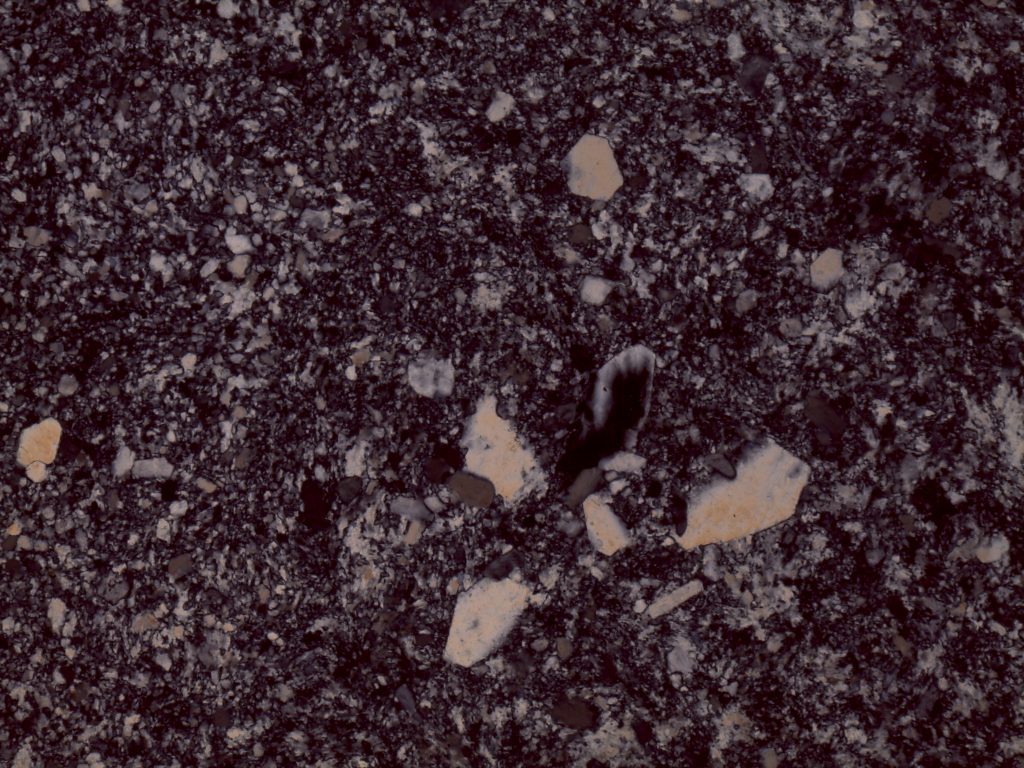
Rock gypsum, plane polars
Rock gypsum, crossed polars