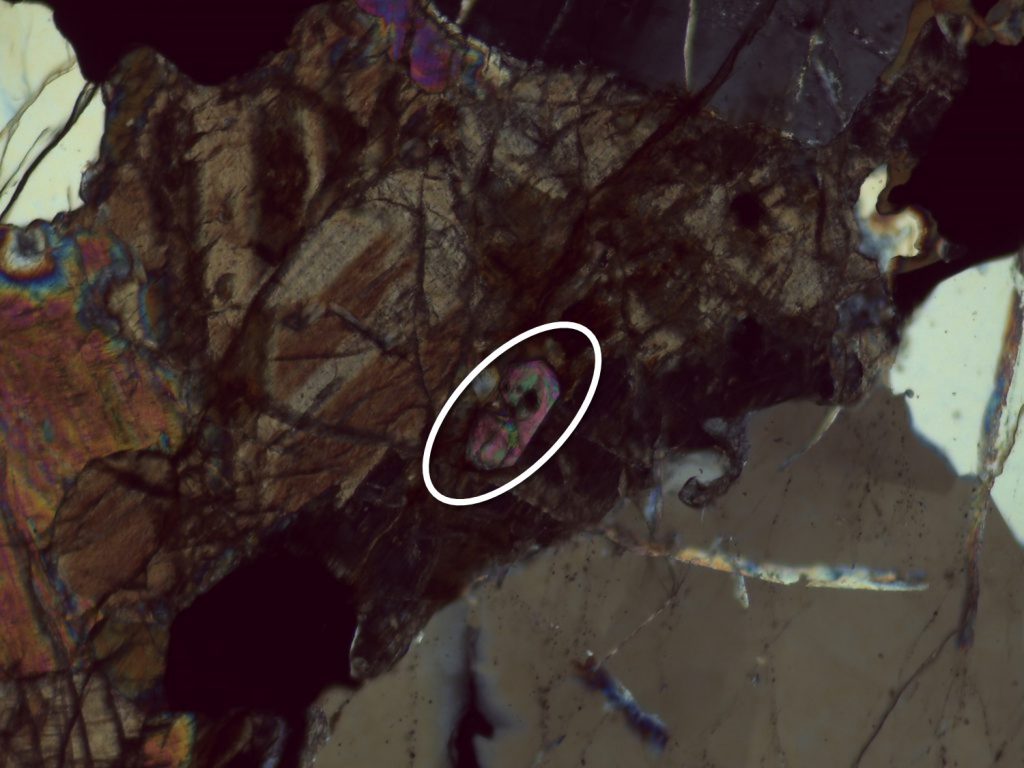Physical Properties |
|
| Chemical formula | Ca2(Al,Fe)3Si3O12(OH) |
| Class | Sorosilicate Paired tetrahedra groups |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Habit | Prismatic Fibrous Acicular Granular Massive Fibrous aggregates |
| Color | Pistachio green Yellow-green to black |
| Hardness | 6 to 7 |
| Specific gravity | 3.4 to 3.5 |
| Cleavage | Perfect (001), poor (100) |
| Fracture | Uneven |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent |
| Streak | White |
Optical Properties |
|
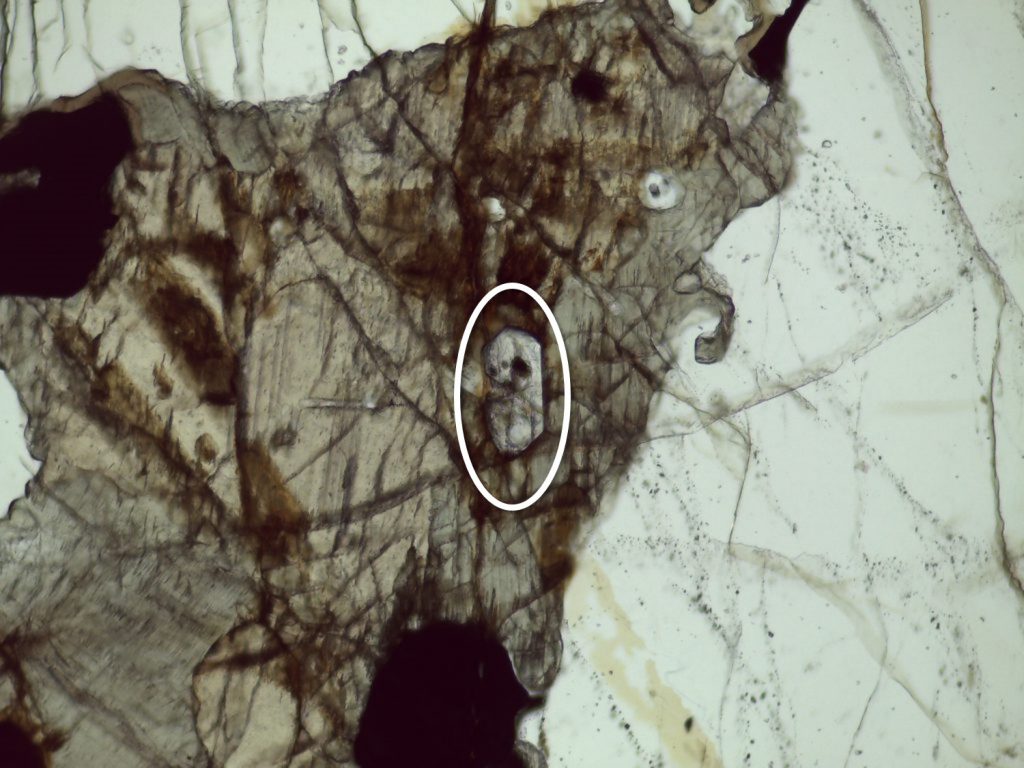
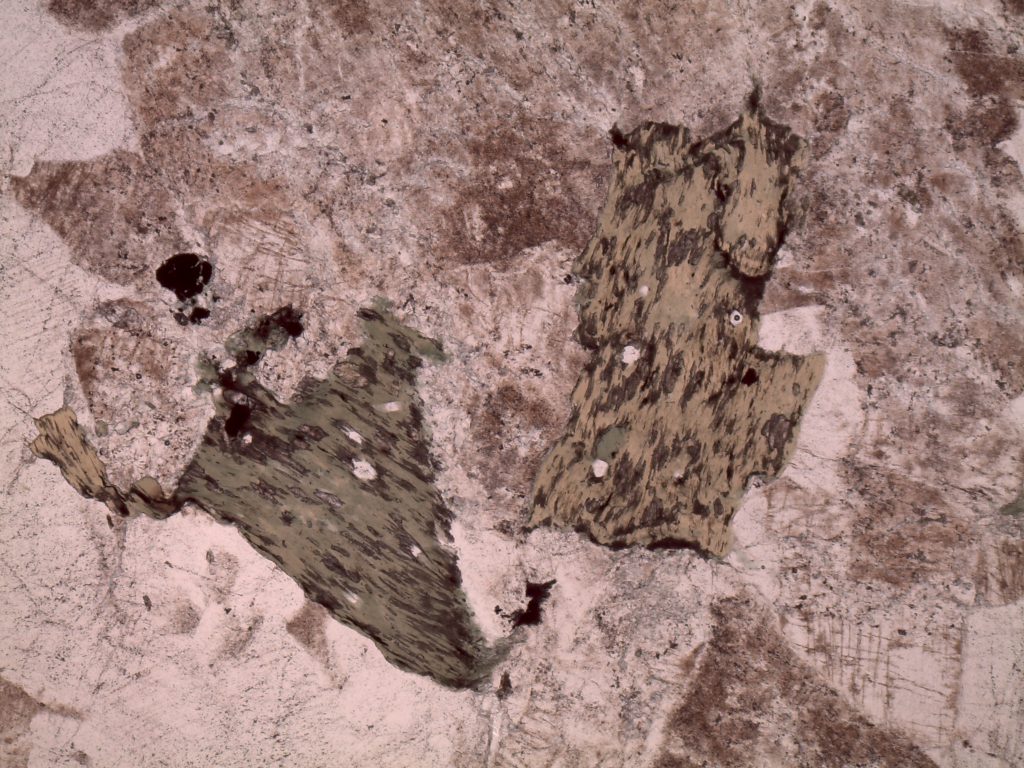
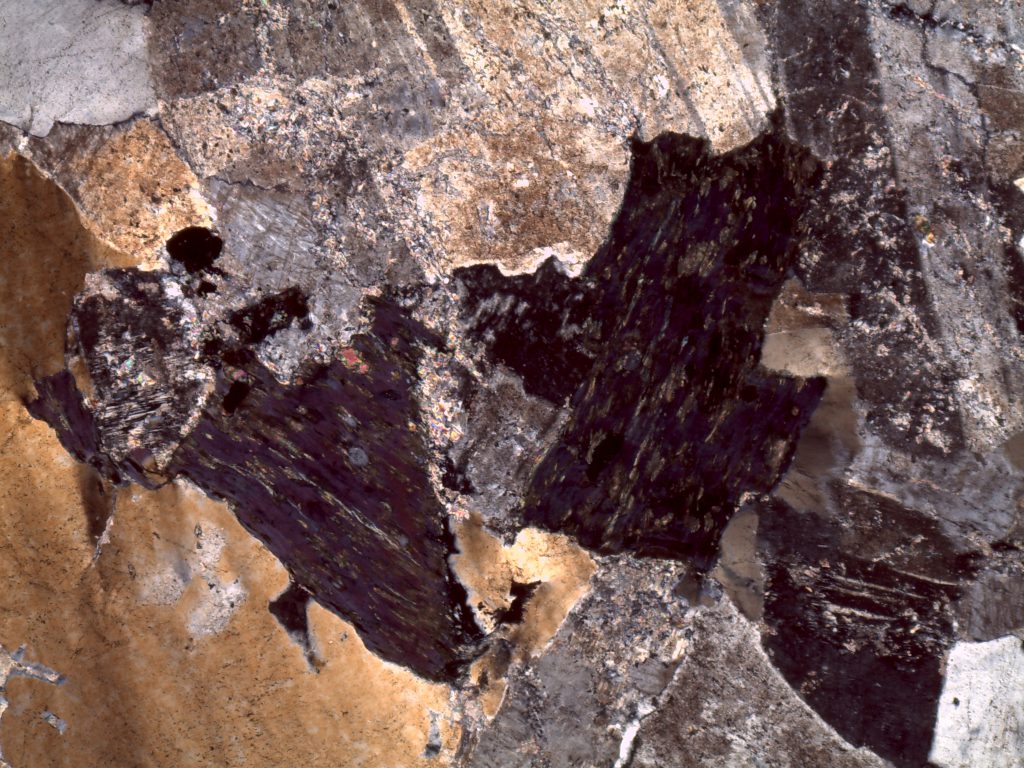
| PPL | Usually colorless; may be light green or pink, depending on composition Typically non-pleochroic High relief |
| XPL | Up to 3rd order colors with increasing Fe content Football-shaped Concentric color rings |
| δ | 0.01 |
| after Perkins, 350 |
Epidote in Hand Sample
Epidote in unakite
Epidote in a different unakite
Epidote in Catoctin Formation metabasalt
Epidote-family mineral zoisite, with black hornblende and red corundum (ruby)
Epidote marking a fault contact between two gneisses
Epidote in Thin Section
Thin Section GigaPans
Epidote in epidosite, plane polars
Epidote in epidosite, crossed polars
Epidote in unakite, plane polars
Epidote in unakite, crossed polars
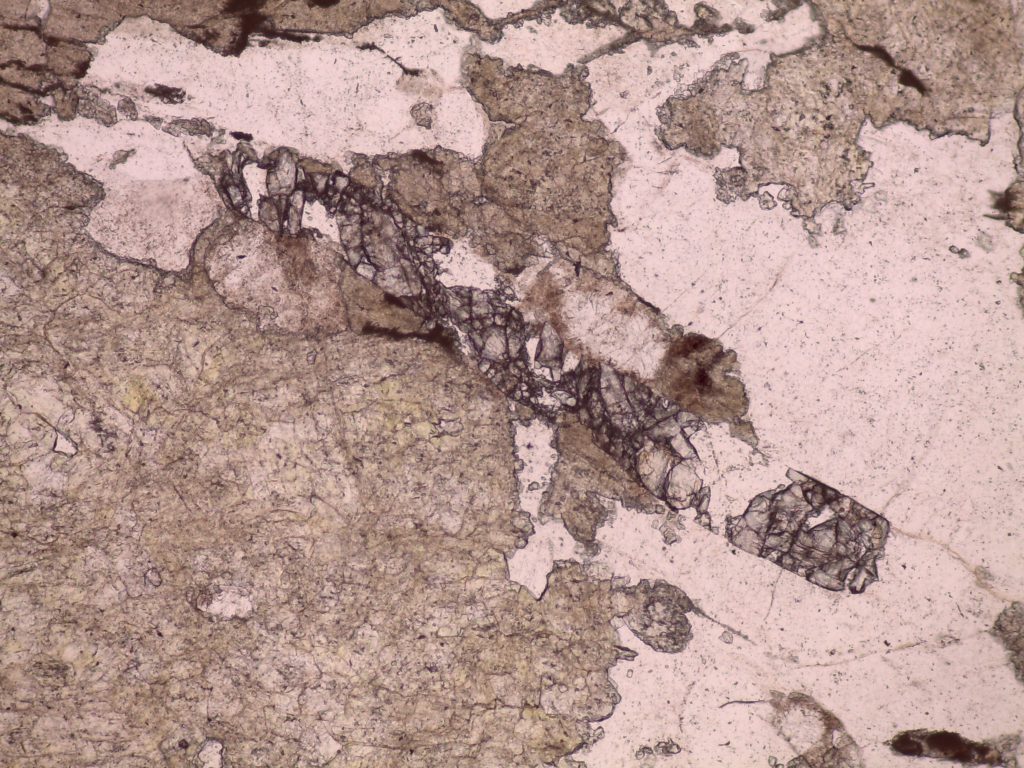
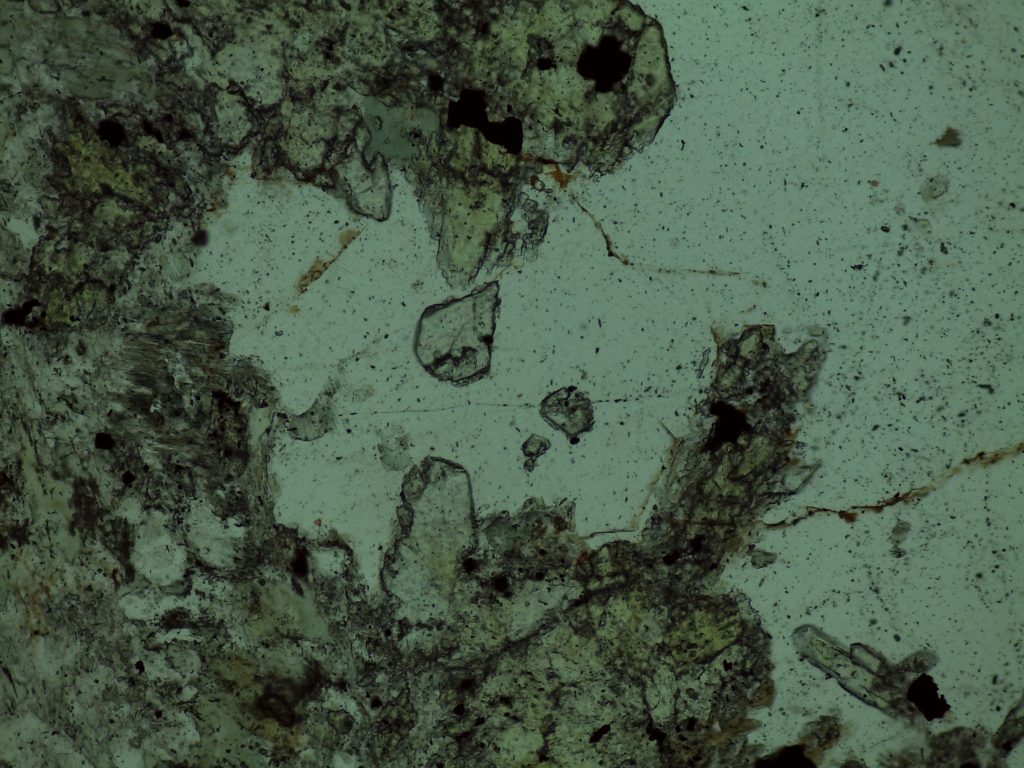
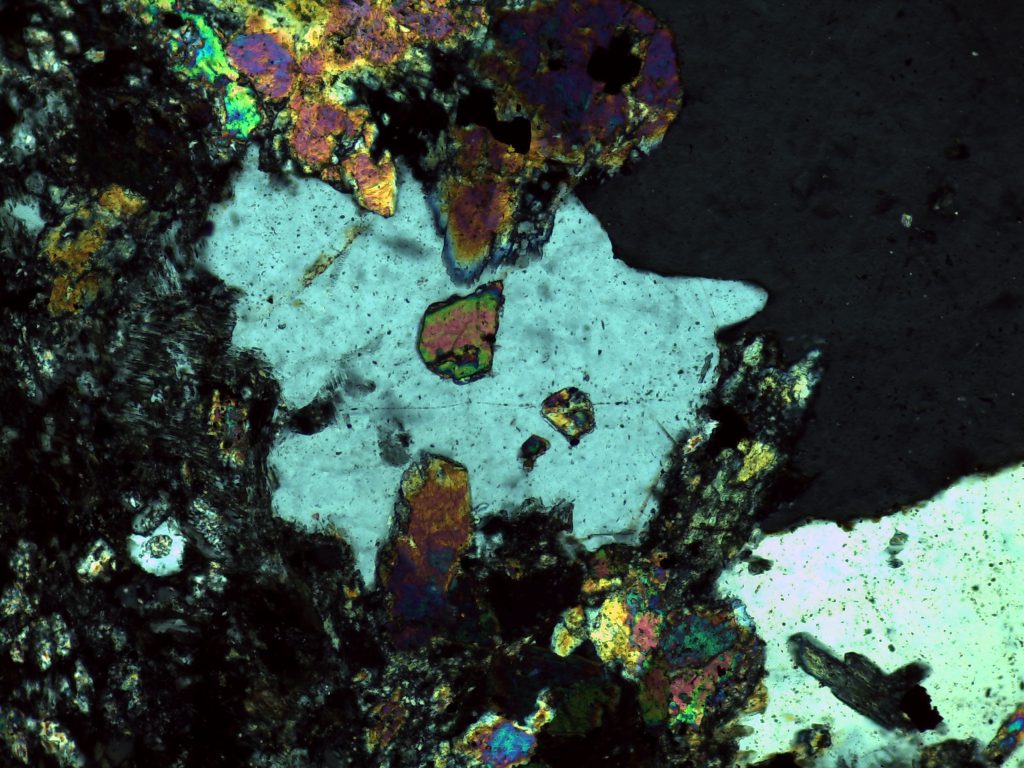

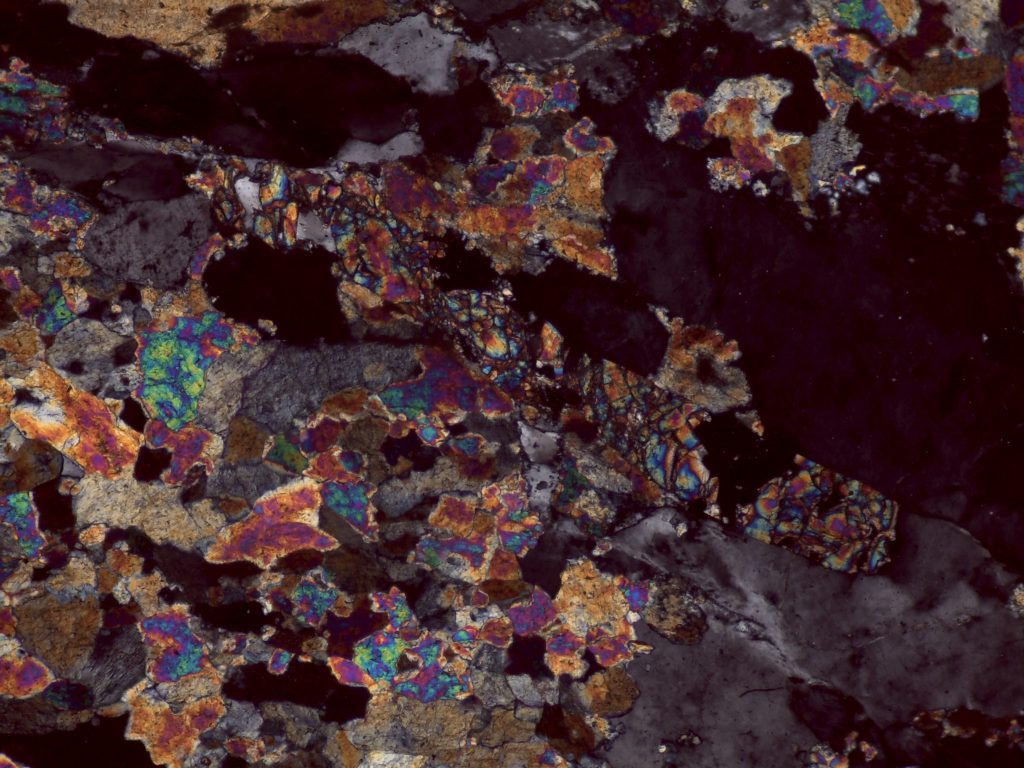
The preceding pictures and videos are of epidote in epidosite and unakite, where it’s quite easy to spot. You’re more likely to encounter epidote as a tiny, easily overlooked accessory mineral; the following pictures and videos are of tiny, easily overlooked accessory epidote.