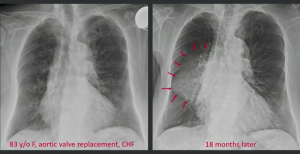
Unlocking the DNA sequence was celebrated in the early 2000s as providing the key to curing disease. Overlooked is the relative lack of information about the structure of folded proteins. Most of the known protein structures studied are bacterial; of all the known protein structures, only 25% are human (2017 data). The proteins in our bodies are responsible for everything from sending signals in autoimmune disease to driving the uncontrolled growth in cancer. Knowing the structure of proteins allows researchers to design and build drugs that impair their action.
You can contribute to unlocking the structure of proteins with your desktop/laptop computer and internet connection. Through the Folding@Home research project run by a Stanford professor, you can load a free program onto your computer that runs in the background. Using your computer’s processing power, folding simulations are run and the data you generate contributes to research. The program runs mathematical calculations to determine how the proteins will fold in the most energetically favorable shape. By unlocking the computer power of computers all over the world, protein structures can be determined and used by researchers to better understand disease.
foldingathome.org