Case Study: “The Painful Eye Puff”
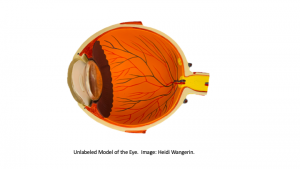
Sagittal section of the eye. Northern Virginia Community College by H.W. is licensed under CC BY 4.0
Emran hasn’t been to the eye doctor in some time, but has noticed that now, at age 54, he can’t read the back of the medication bottle dosage instructions unless he finds bright light and a magnifying glass. He goes to get his eyes checked to see if he would benefit from glasses. At the eye doctor’s office, the nurse on duty asks Emran to place his chin in a tray and stare straight ahead. She moves a small machine close to his left eye and administers an unexpected puff of air into Emran’s eye. She does the same on the right side. Emran yelps in pain. “Oh, that’s painful?” asks the nurse. “I’ll ask the doctor to talk with you about that further”. She guides Emran to the examination room where Emran sits quietly, mulling over what might be going on. Why would his right eye hurt with a harmless puff of air? When Dr. Reddy arrives, she explains that first she will test his vision using the Snellen test and then she will administer atropine, a muscarinic receptor blocker, to cause pupil dilation so she can look into the back of the eye. “What about that puff test?” asks Emran. “Yes, we will discuss that, too,” replies the doctor, “I think we need more tests.”
Objectives
After completing this lab, students will be able to….
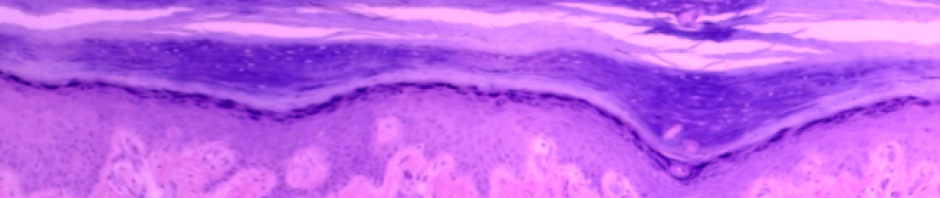
- Identify and describe the function of each of the structures, layers, cavities, and chambers of the eye on an image and on the eye model.
- Trace the path of light through the eye to the retina.
- Identify and label the structures of the retina from a microscope slide and an image.
- Identify the structures (see starred structures* on the anatomical terminology checklist) on a dissected cow’s eye and describe the function of each.
- Compare and contrast the structure and function of the cow eye with a human eye.
- For each of the eye tests, explain 1) how to perform each test, 2) the rationale for each test and 3) normal and abnormal results.
- Given various eye tests, explain what an abnormal test tells you about vision.
Materials
- eye model
- microscope
- microscope slide of retina
- terminology labels
- cow eye
- disposable gloves
- dissecting tray and tools (scissors, scalpel, forceps, blunt probe)
- lab apron
- paper towels
- safety goggles/glasses
- slotted spoon
- dissecting pin or paper clip
- Ishihara color plates
- meter stick or centimeter ruler
- Snellen eye chart
*Note* This lab contains two Case Studies and focuses on two of the special senses, eyes and ears.
Case Study: “To hear or not to hear?”
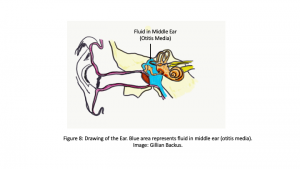
Sagittal section of the ear. Northern Virginia Community College by G.B. is licensed under CC BY 4.0
You are a nurse helping in an audiologist’s office. This morning, your patient is a 2-year-old girl, named Anne. Her mother complains that her daughter doesn’t respond to sound, even loud sounds, and she is worried that her daughter’s stubborn behavior is more than just the terrible twos, but an inability to hear. Her mother also reports that her speech development is delayed, noting that her vocabulary seems stunted compared to other children in her day care room, and that she seems to have trouble forming some of her letters. In all other ways, the little girl is alert and oriented, responds well to attention and has normal vital signs. First you examine the anatomical structures of her ear using an otoscope and then proceed to administering a number of hearing tests.
Objectives
After completing the lab, students will be able to…
- Identify and state the functions of each of the structures of the ear (see the terminology checklist) on an image and on the ear model.
- Trace the path of sound as it travels from the outer ear to the inner cochlea, and label each anatomical structure involved.
- Define and differentiate between conductive deafness and sensorineural deafness.
- For the Romberg test 1) describe how to perform the test, 2) the rationale for the test and 3) normal and abnormal results with respect to equilibrium and proprioception (3D awareness).
Materials
- ear model
- ear terminology labels with sticky tack
- diagram of an ear
- rubber activator
- tuning fork
- blackboard or chalkboard
- dry erase marker or chalk
Try the lab!
12 Special Senses Lab summer 2022 CC
Instructor Resources
Need something? Want to leave a comment or question? Fill in the contact form below:
![]()
A&P 1 OER Lab Manual © 2022 by H. Wangerin, P. Rodgers, G. Backus is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0