Case Study: “The Pain in the Back”
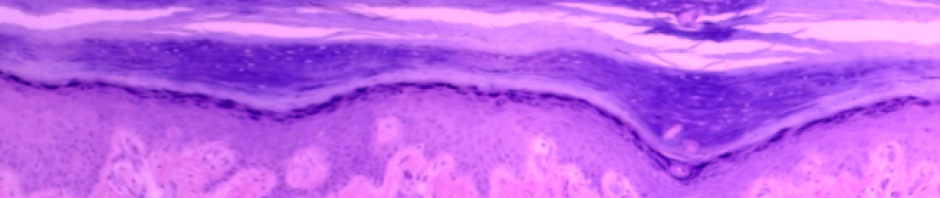
Histology of cross-section of spinal cord with highlighted ependymal cells of the central canal. Northern Virginia Community College by H.W. is licensed under CC BY 4.0
You are a nurse practitioner working in a family practice. One of your patients, Adele, a young woman in her 20’s, comes in with pain in her lower back and pain down the anterior and posterior of her leg. She remarks that the pain began shortly after she began a weightlifting regimen. The pain is quite severe, preventing her from lying down at night and disrupting her sleep. She has been struggling to walk upstairs and a number of times her leg has buckled (given out) from under her. She asks for medication for pain relief that will allow her to sleep. You suspect a herniated disc in which the intervertebral disc, the pad of fibrocartilage between the vertebrae, has ruptured and is putting pressure on the several spinal nerves. You write a referral for an MRI and schedule an appointment with the radiologist to have her lower back imaged the following day.
Background
In this lab, students will learn the anatomical components of the spinal cord, learn the names of the spinal nerves, and how they are arranged in plexi. They will learn to identify the brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexi. Lastly, they will study the anatomy and physiology of two types of reflexes: one autonomic and one somatic reflex.
Objectives
By the end of the lab, students will be able to identify the…
Spinal Cord
- From a cross section of the spinal cord (microscopic specimen, digital image, and model) identify the structures from the terminology checklist.

Image of a cross-section of a spinal cord. Northern Virginia Community College by H.W. is licensed under CC BY 4.0
- Describe the functions of the following parts of the spinal cord: posterior horn, lateral horn, and anterior horn.
- Identify the various structural components of the spinal cord (conus medullaris, cauda equina, filum terminale)
Spinal Nerves
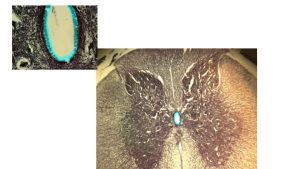
- Name and describe the location of the four main spinal nerve plexuses.
- Locate, identify and describe the function of specific peripheral nerves on an image or model and match it with its corresponding nerve plexus.
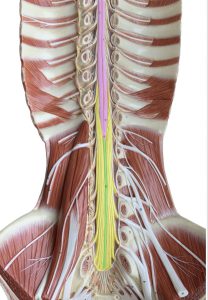
Spinal Cord Longitudinal Section © 2022 by H. Wangerin is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0
Spinal Reflexes
- Define and cite examples of both a somatic reflex and an autonomic reflex
- Identify the specific nerves and structures involved in the following reflex arcs: patellar reflex and pupillary light reflex (PLR).
- Identify the components of a reflex on an image and describe the function of each component.
- Evaluate a normal versus an abnormal response to a reflex test.
- Given an abnormal response to a specific reflex, predict the damaged nerve or anatomical structure.
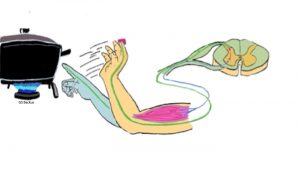
Reflex Arc touching a hot stove. Northern Virginia Community College by Gillian Backus is licensed under CC BY 4.0
Materials
- compound microscope
- histology slide of spinal cord cross section
- isopropyl alcohol
- lens paper
- colored pencils
- laminated terminology labels with sticky tack
- spinal cord cross section model
- pen light
- reflex hammer
Ready to try the Lab?
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lab (Su23)
Instructor Resources
Need something? Want to leave a comment? Fill out the contact form!
![]()
A&P 1 OER Lab Manual © 2022 by H. Wangerin, P. Rodgers, G. Backus is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0